Strong acids and bases are essential in many laboratory and industrial settings. These chemicals require special handling and storage. Improper storage can lead to dangerous accidents. PP safety cabinets provide the ideal solution for these hazardous materials. Learning how to safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets is crucial for workplace safety. This guide will walk you through the best practices and procedures. When you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets, you protect both people and property.
Understanding PP Safety Cabinets for Chemical Storage
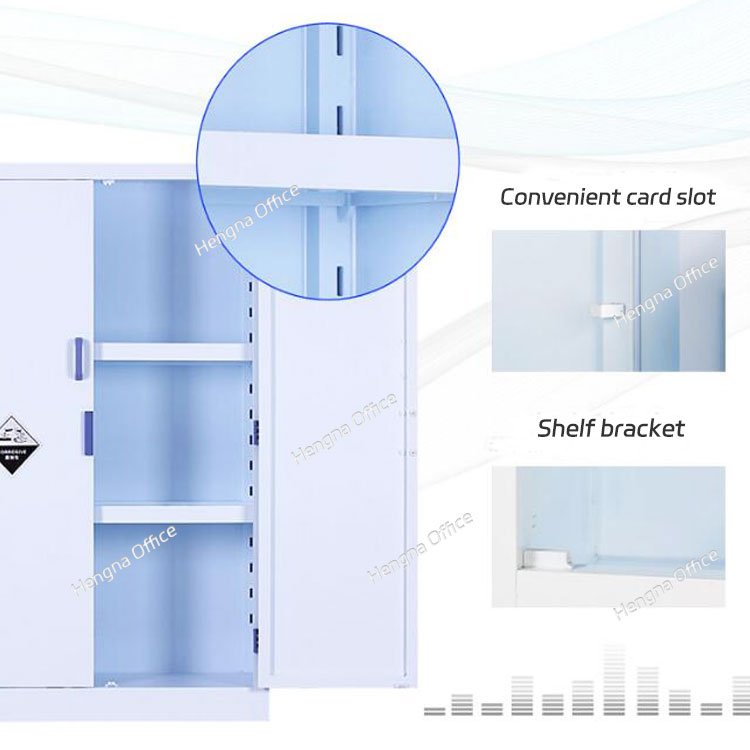
PP safety cabinets are specifically designed for corrosive chemicals. PP stands for polypropylene, a highly resistant material. This material withstands corrosion from strong acids and bases. Unlike metal cabinets, PP won’t degrade when exposed to these chemicals. PP safety cabinets feature seamless construction and leak-proof designs. These cabinets are essential for any facility handling corrosive substances. When you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets, you ensure long-term protection. The durability of PP safety cabinets makes them a wise investment for chemical storage.
Key Features of PP Safety Cabinets:
- Corrosion-resistant construction throughout the entire cabinet
- Seamless interior design that prevents leaks and spills
- Adjustable shelving for flexible organization of chemicals
- Ventilation systems in some models for fume control
- Locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access
- Chemical-resistant materials that won’t degrade over time

Types of Strong Acids and Bases Requiring Special Storage
Many common chemicals require storage in PP safety cabinets. Strong acids include sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid. These substances can cause severe burns and damage equipment. Strong bases like sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide are equally hazardous. Both categories of chemicals can react dangerously with other substances. PP safety cabinets provide the necessary containment for these materials. Always identify which chemicals in your facility need PP safety cabinet storage. Proper identification is the first step to safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets.
Common Strong Acids and Bases Requiring PP Safety Cabinets:
| Strong Acids | Strong Bases |
|---|---|
| Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) | Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) |
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) |
| Nitric Acid (HNO₃) | Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) |
| Acetic Acid (CH₃COOH) | Ammonium Hydroxide (NH₄OH) |
| Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | Barium Hydroxide (Ba(OH)₂) |
Best Practices for Safely Storing Strong Acids in PP Safety Cabinets
Strong acids require specific handling procedures in PP safety cabinets. Always store acids in their original containers when possible. Make sure containers are tightly sealed before placement. Label all containers clearly with contents and hazard information. Store acids away from incompatible materials like bases or oxidizers. PP safety cabinets should be placed in well-ventilated areas. Regular inspection of containers and cabinets is essential. These practices help you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets. Following these procedures minimizes risks associated with acid storage.
Steps to Safely Store Strong Acids:
- Inspect containers for damage or leaks before storage
- Verify labels are clear and include hazard information
- Seal containers tightly to prevent vapor release
- Place containers in secondary containment trays within the cabinet
- Organize by compatibility, not alphabetically
- Maintain proper spacing between containers to prevent tipping
- Document storage locations in your chemical inventory system
Proper Techniques for Storing Bases in PP Safety Cabinets
Bases need similar careful handling in PP safety cabinets. Like acids, bases should remain in their original, properly sealed containers. Clear labeling is crucial for all base containers. Store bases separately from acids to prevent dangerous reactions. PP safety cabinets provide the necessary separation for these chemicals. Ensure that cabinet shelves are level and secure to prevent tipping. Regular maintenance of PP safety cabinets ensures continued protection. These techniques are vital when you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets. Proper base storage prevents accidents and extends cabinet life.
Base Storage Safety Checklist:
- [ ] Containers are in good condition without cracks or damage
- [ ] All containers have legible, accurate labels
- [ ] Bases are stored separately from acids and oxidizers
- [ ] Cabinet shelves are secure and level
- [ ] Secondary containment trays are in place
- [ ] Inventory records are up-to-date
- [ ] Access is restricted to authorized personnel only
Organization Strategies for PP Safety Cabinets
Effective organization maximizes the safety of PP safety cabinets. Group chemicals by compatibility rather than alphabetically. Use secondary containment trays within PP safety cabinets for extra protection. Implement an inventory system to track all stored chemicals. Keep access logs to monitor who uses the cabinet and when. Train all personnel on proper organization procedures. Regular audits help maintain organization standards. Good organization practices are essential to safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets. A well-organized cabinet reduces the risk of accidents and improves efficiency.
Chemical Compatibility Groups for PP Safety Cabinets:
- Mineral Acids (sulfuric, hydrochloric, nitric)
- Organic Acids (acetic, formic, propionic)
- Caustics/Bases (sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide)
- Oxidizing Agents (peroxides, chlorates, nitrates)
- Flammable Materials (alcohols, ketones, solvents)
- Reducing Agents (sulfites, hydrazine, metal powders)
Safety Procedures When Using PP Safety Cabinets
Following proper safety procedures is crucial when working with PP safety cabinets. Always wear appropriate PPE when accessing stored chemicals. Know the location of emergency equipment like eyewash stations. Never work alone when handling strong acids or bases. Keep cabinet doors closed except when accessing materials. Report any damage or leaks immediately. These procedures ensure you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets. Consistent adherence to safety protocols protects everyone in the facility.
Required PPE for Handling Strong Acids and Bases:
- Chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile or neoprene)
- Safety goggles or face shield for eye protection
- Lab coat or chemical-resistant apron
- Closed-toe shoes with chemical-resistant soles
- Respirator (if ventilation is insufficient)
Regulatory Compliance for PP Safety Cabinet Storage
Various regulations govern the storage of strong acids and bases. OSHA and EPA provide specific guidelines for chemical storage. Local fire codes may have additional requirements for PP safety cabinets. Regular inspections ensure compliance with these regulations. Proper documentation of storage practices is essential. Training records should be maintained for all personnel. Compliance is a key aspect when you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets. Meeting regulatory requirements protects your facility from fines and legal issues.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with PP Safety Cabinets
Several common mistakes can compromise the safety of PP safety cabinets. Overloading cabinets beyond their capacity is a frequent error. Storing incompatible chemicals together creates dangerous situations. Neglecting regular maintenance leads to cabinet deterioration. Failing to train personnel on proper procedures increases risks. Ignoring minor leaks can result in major accidents. Avoiding these mistakes helps you safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets. Awareness of common pitfalls prevents many storage-related incidents.
Top 5 Storage Mistakes to Avoid:
- Overloading shelves beyond weight capacity
- Mixing incompatible chemicals in the same cabinet
- Skipping regular inspections and maintenance
- Inadequate staff training on proper procedures
- Ignoring small leaks or signs of cabinet damage
Maintenance and Inspection of PP Safety Cabinets
Regular maintenance keeps PP safety cabinets functioning properly. Inspect cabinets weekly for signs of damage or corrosion. Check door seals and locking mechanisms regularly. Clean cabinet interiors as needed to prevent chemical buildup. Test ventilation systems if your cabinet includes them. Address any issues immediately to maintain safety. Proper maintenance ensures you can safely store strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets for years to come. A well-maintained cabinet provides reliable protection against chemical hazards.
Weekly Inspection Checklist:
- [ ] Check for visible signs of corrosion or damage
- [ ] Test door seals and locking mechanisms
- [ ] Verify ventilation systems are functioning
- [ ] Inspect shelves for stability and level position
- [ ] Check secondary containment trays for cracks
- [ ] Review chemical inventory for expired items
- [ ] Document inspection results and any actions taken
Safely storing strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets requires attention to detail. Proper procedures, regular maintenance, and thorough training are essential. PP safety cabinets provide the protection needed for these hazardous materials. By following the guidelines outlined here, you create a safer work environment. Remember that safely storing strong acids and bases in PP safety cabinets is an ongoing responsibility. Make safety a priority in your chemical storage practices. Your commitment to proper storage protects everyone in your facility.



